RAW can mean several things with regards to data recovery; ‘You can recover your RAW photos from a SD Card with a RAW file system using RAW file recovery’.
With regards to file and photo recovery, RAW data recovery can refer to three different things:
- The recovery method; RAW vs. file system based recovery
- It may refer to the state of the file system, ‘RAW’.
- The file format of a digital photo.
RAW data recovery: the recovery method
There are two methods to recover deleted and lost data
The first method is file system based: The recovery software will try reconstructing a virtual file system from which files can be copied to another drive. By working out the start of the file system and the cluster size the locations of files as defined in file entries can be determined. File names can be determined from those entries. It is often also possible to reconstruct the directory structure.
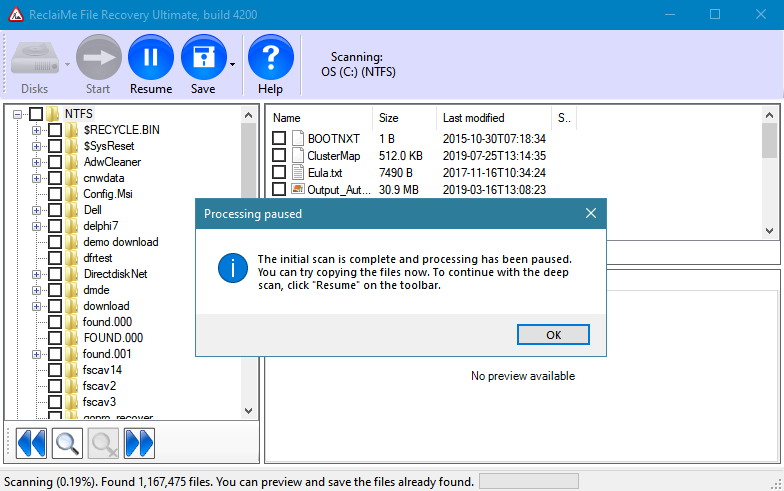
File system based file recovery from a RAW file system. File names and directory structure are recovered too.
RAW data recovery being the second method on the other hand ignores the file system and scans a drive for characteristics for specific file types. These characteristics are often specific byte sequences which are common for one specific file type. The byte sequences are called magic bytes or magic numbers. This method only allows for recovery of files the software knows magic bytes for.
RAW data recovery software is also referred to as a carver and the process of detecting and recovering photos using this method as carving.
To a degree RAW data recovery software may still try to find a solution for the start of the file system and the cluster size as it can greatly reduce scan times.
| File system based vs. RAW data recovery | |
| File system based file recovery | RAW data recovery |
| Recovers directory structure | Does not recover directory structure |
| Original file names and attributes | File names are not recovered |
| Success depends on state of file system | Even recovers data if file system is FUBAR |
| Recovers any file type | Only recovers specific file types |
| File system can be reconstructed within minutes* | Slow |
| No need to scan the entire volume | Entire drive needs to be scanned |
| File fragmentation is no issue** | Fragmented files are problem |
* – Depends on file system state
** – Depends on file system
File system: State of the file system is RAW
In order for an OS to be able to work with a file system, it has to parse the file system structure. Starting with the boot record the OS works out the start of the file system and cluster size. The boot record also contains pointers to clusters containing following structures such as the master file table (MFT). The whole process is also referred to as ‘mounting’.
Now if the boot record for example contains an invalid value for cluster size the OS will fail to find the MFT. If Windows is unable to mount the file system due to corruption in one of these meta structures is designates the file system as ‘RAW’.
Very often file system based recovery is possible however on memory cards used in cameras the RAW recovery method is some times required and more successful.
RAW photo file format(s)
RAW photos are files that contain all sensor data from the often more expensive digital cameras For example Canon cameras produce CR2 files, Nikons store their sensor data in NEF files and Sony cameras in files with the extension ARW. They tend to be quite large. You can look at those files as digital negatives that require further processing using a RAW developer to produce a nice picture of an acceptable file size.
RAW photos are often specific to a brand of camera but often based on the TIFF file structure.
If RAW photos need to be recovered from a hard drive the best way to do this is by using file system based recovery software. In many situations you can also use this generic software to recover data from memory cards. This being said, memory cards is where the RAW recovery method can really shine. If file system based recovery software fails to recover your lost or deleted photos from an SD Card then do not give up before having tried RAW file recovery.