Disk Drill 6 — Scan Modes Explained
A practical, no-fluff guide to how Disk Drill finds files and which scan mode to pick.
How Disk Drill finds lost files
Disk Drill uses two fundamentally different detection methods. Understanding them helps you pick the right scan mode and saves time during recovery.
1. File system–based recovery
When files are deleted, the data often remains on the drive — only the file system reference is gone. Disk Drill reads file system metadata (for example, NTFS MFT entries or FAT/exFAT directory records) to reconstruct a virtual file system. This method is fast and can restore:
- original file names
- folder structure
- timestamps
2. Raw (signature) scan
If the file system metadata is missing or corrupted, Disk Drill can scan the device byte-by-byte and look for known file signatures (JPEG headers, MP4/ MOV markers, DOCX containers, etc.). This raw scan:
- does not rely on a working file system
- is considered a last resort option
- often cannot restore original names or folders (though it may infer names from embedded metadata like EXIF)
Disk Drill 6 Scan Modes
Quick Scan
Method: File system metadata reconstruction.
What it finds: Recently deleted files and files on a deleted/lost partition (as long as metadata is present).
When to use: You emptied the Recycle Bin or removed files recently. But also, scan a lost partition with an intact file system
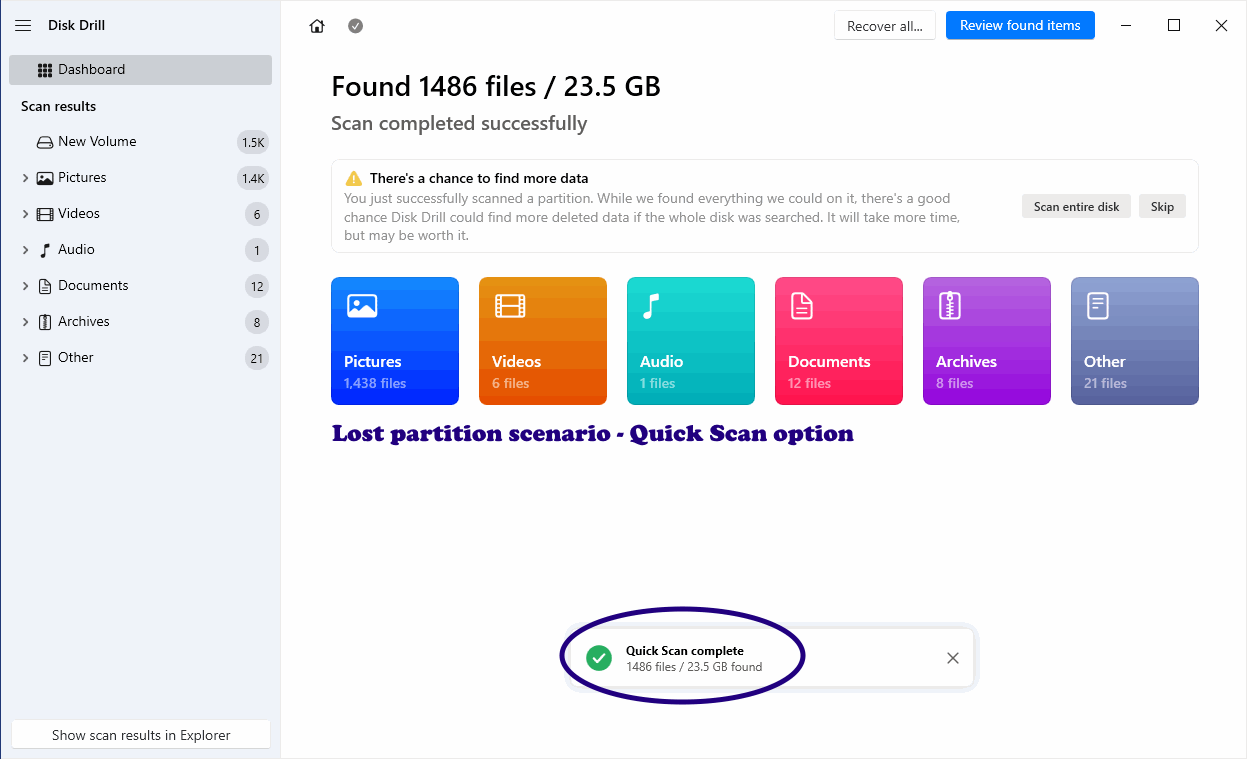
Deep Scan
Method: Raw signature-based scan.
What it finds: Files by signature even if the file system is damaged or missing. May infer names from EXIF or embedded metadata, but original folder tree is lost.
When to use: When other can modes yield no result.
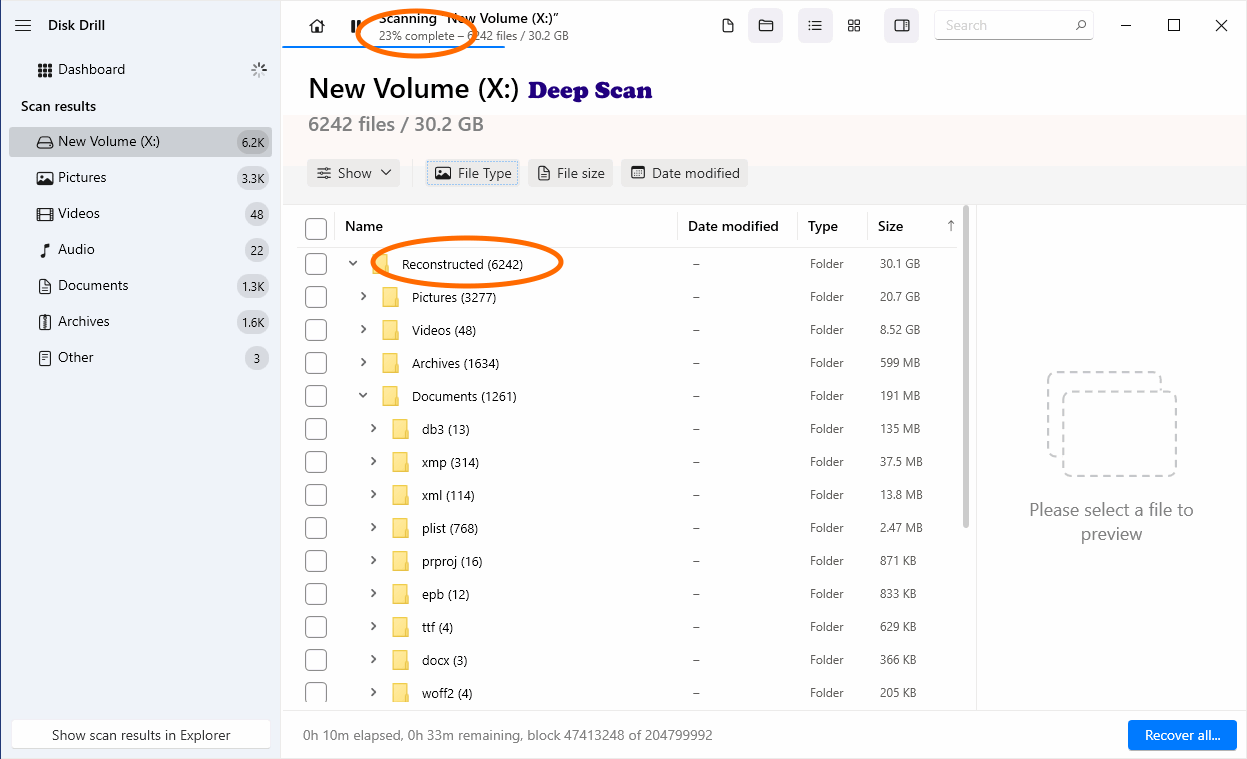
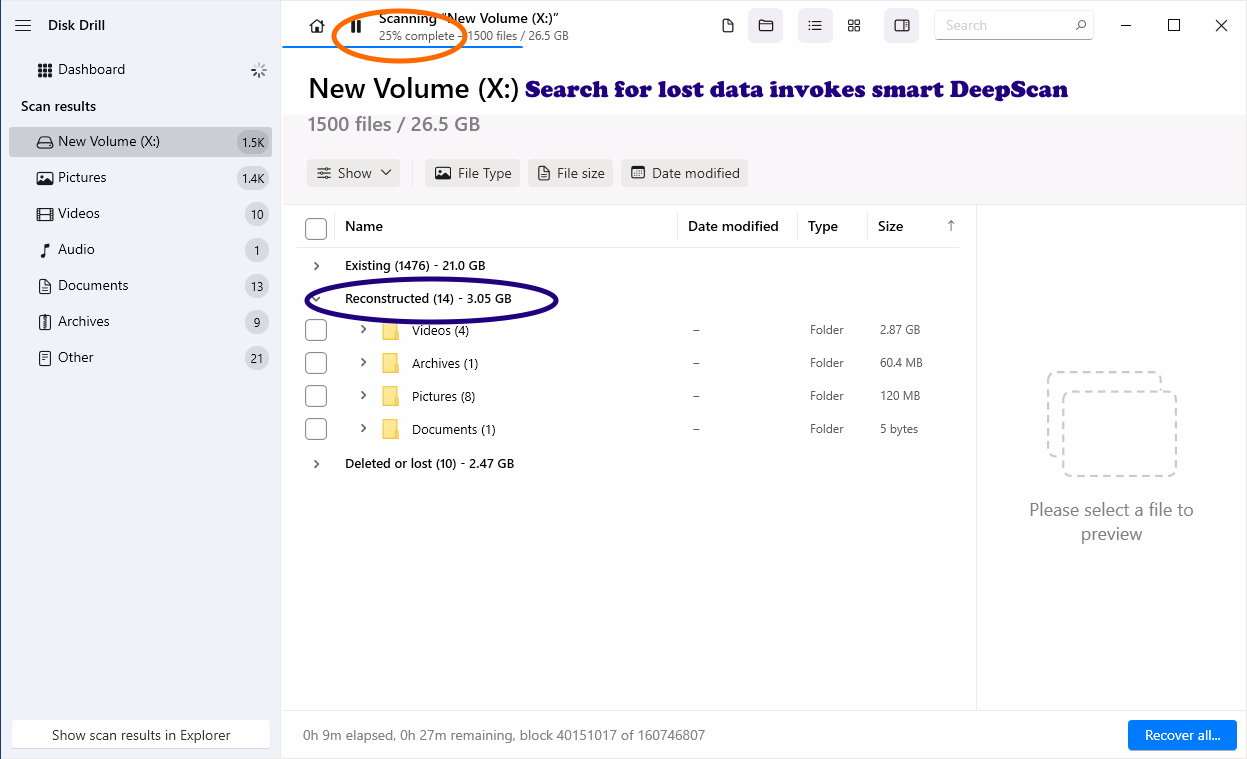
Search for Lost Data
Method: Hybrid — uses file system reconstruction and performs a deep scan only in empty/unallocated space.
What it finds: Existing, reconstructed and deleted/lost files with faster deep-scan coverage where it counts.
When to use: You want a thorough but time-efficient scan that balances speed and reach. This is the default scan mode in Disk Drill
Allocate Existing
Method: File system metadata reconstruction.
What it finds: Existing data referenced in the file system.
When to use: Some times minor file system corruption prevents data access, this method may help you access your files without the need for scans
Advanced Camera Recovery
Method: Signature-based scan, file meta data analysis, pattern analysis.
What it finds: Still and video footage on corrupt, formatted, etc. memory cards
When to use: To recover photo and video footage produced by hi-res and action cameras from memory cards.
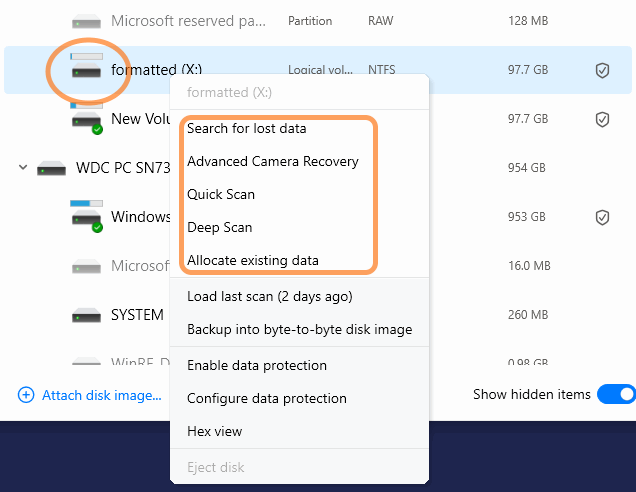
How to Start Different Scan Modes in Disk Drill 6
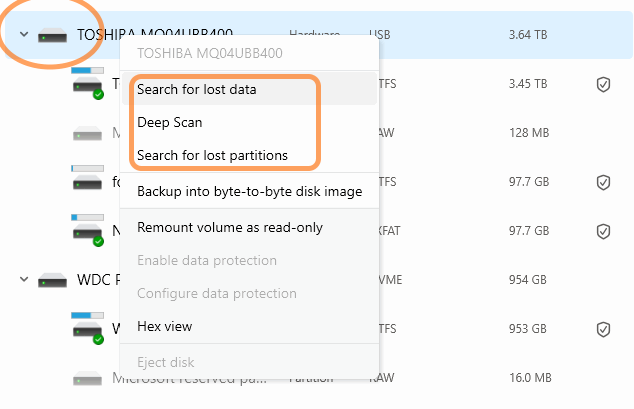
Disk Drill organizes scan modes based on whether you right-click a physical drive or a partition. Here’s a quick guide:
When you right-click a physical drive (like Toshiba or WDC):
- Search for Lost Data — performs a combined scan on the entire physical disk.
- Deep Scan — runs a full signature-based raw scan across the whole drive.
- Scan for Partitions — locates lost or deleted partitions before scanning them individually.
When you right-click a partition (like C:, D:, or a recovered partition):
- Search for Lost Data — scans for deleted or lost files within that specific partition.
- Advanced Camera Recovery — specialized scan for photos and videos on that partition, great for SD cards and camera media.
- Quick Scan — fast recovery of recently deleted files on that partition.
- Deep Scan — signature-based recovery limited to the selected partition.
- Allocate Existing Data — lists all files currently accessible by the OS on that partition.
Not sure which Disk Drill 6 scan mode to choose?
Different types of data loss require different recovery approaches. Whether you’ve accidentally deleted a file, lost an entire partition, or need to recover fragmented 4K video from a camera card, picking the right scan mode can save you time and improve results. The table below lists the most common data loss scenarios, along with the recommended Disk Drill scan mode and why it works best.
| Data Loss Scenario | Recommended Scan Mode | Why This Mode Works Best |
|---|---|---|
| Accidentally deleted files from a visible partition | Quick Scan | Uses file system metadata to quickly restore recently deleted files with original names and folders. |
| Deleted or lost partition | Scan for Lost Partition → Quick Scan on found partition | First locates the missing partition, then uses Quick Scan to recover files with original structure if file system metadata is intact. |
| Formatted drive | Search for Lost Data | Recovers both existing and deleted files, scans empty space, and reconstructs folder structure when possible. |
| Severe file system corruption or no file system detected | Deep Scan | Signature-based scan finds files without relying on the original file system. |
| Lost photos/videos from SD card or camera media | Advanced Camera Recovery | Optimized for modern high-res and action cameras; can reconstruct fragmented video files and recover stills even from damaged file systems. |
| Only need to list visible files (for backup or copy) | Allocate Existing | Shows files currently visible to the OS without scanning deleted or lost data. |